PPT Narrow Complex Tachycardias PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID456264

AVRT and AVNRT YouTube
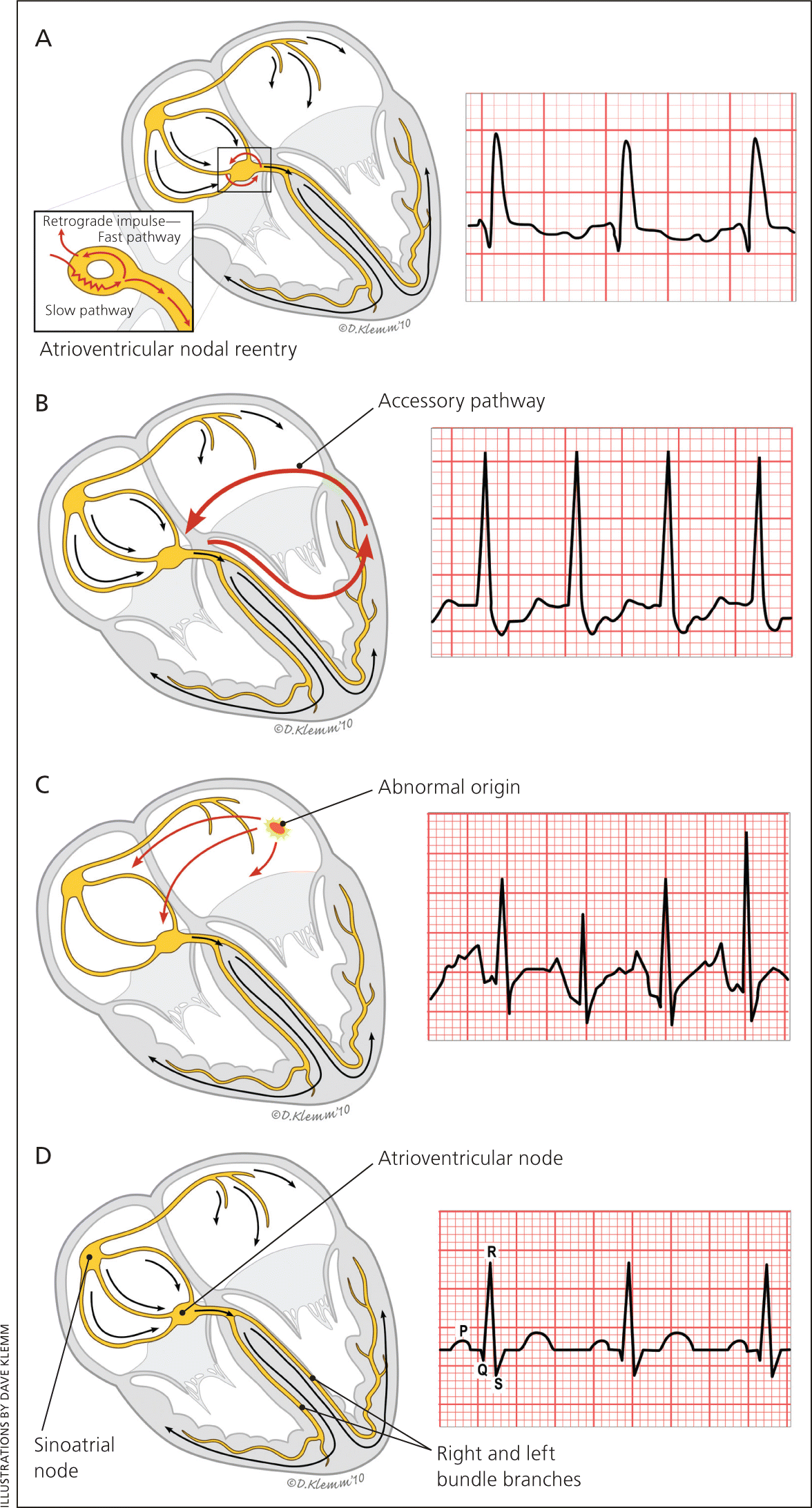
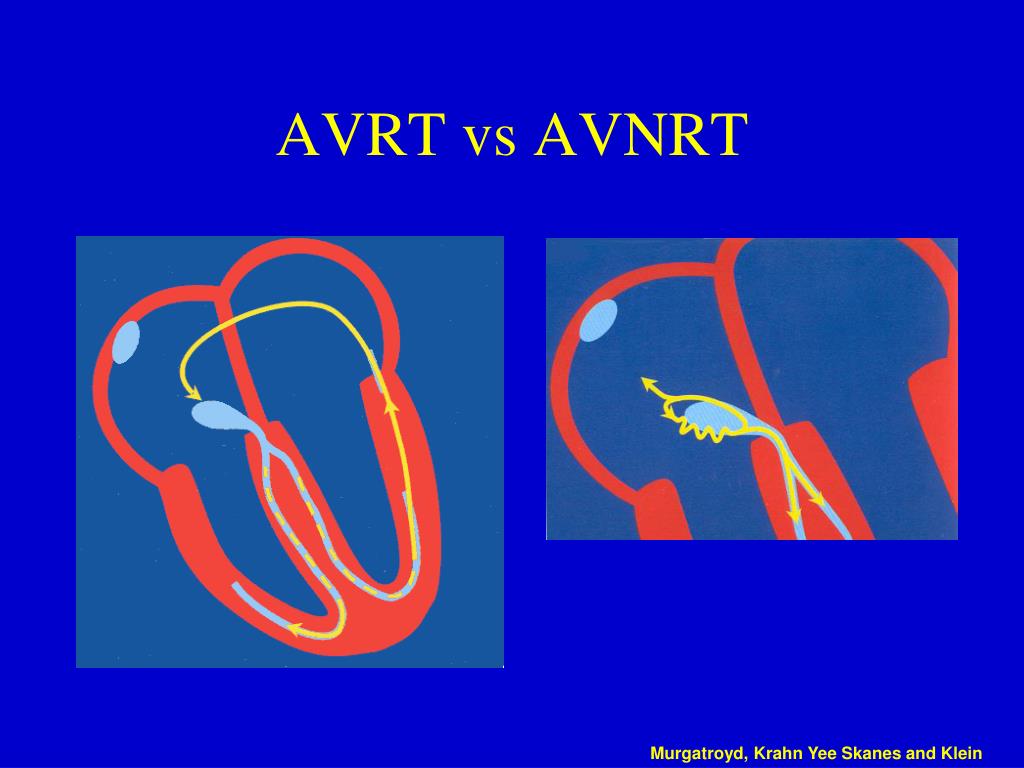
With an atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia, or AVRT, the electrical signal actually uses a separate accessory pathway to get back up from the ventricles to the atria, which causes the atria to contract before the SA node sends out another signal. The signal then moves back down the AV node to the ventricles and purkinje fibers, contracts.
Supraventricular Tachycardia Types Cardiology Outlines
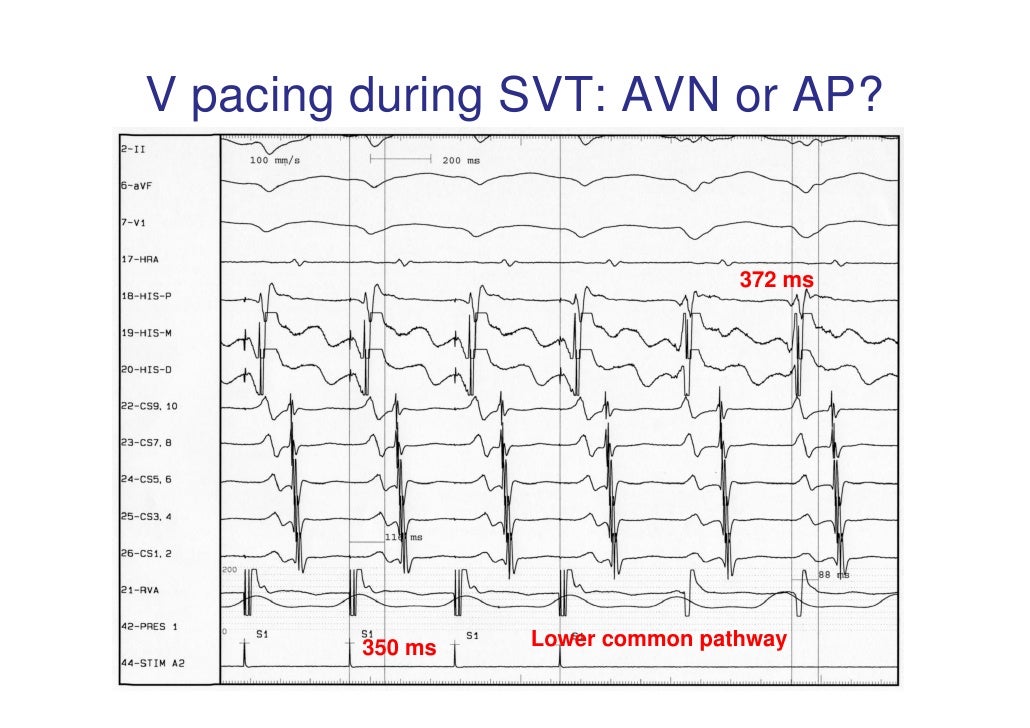
AVNRT vs. AVRT due to septal accessory pathways. The eccentric retrograde atrial activation during ventricular stimulation or tachycardia and the demonstration of continuous AV or VA conduction curves usually characterizing non-septal concealed accessory pathways differentiate this form of atrioventricular re-entry from AVNRT. However, AVNRT is.
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment
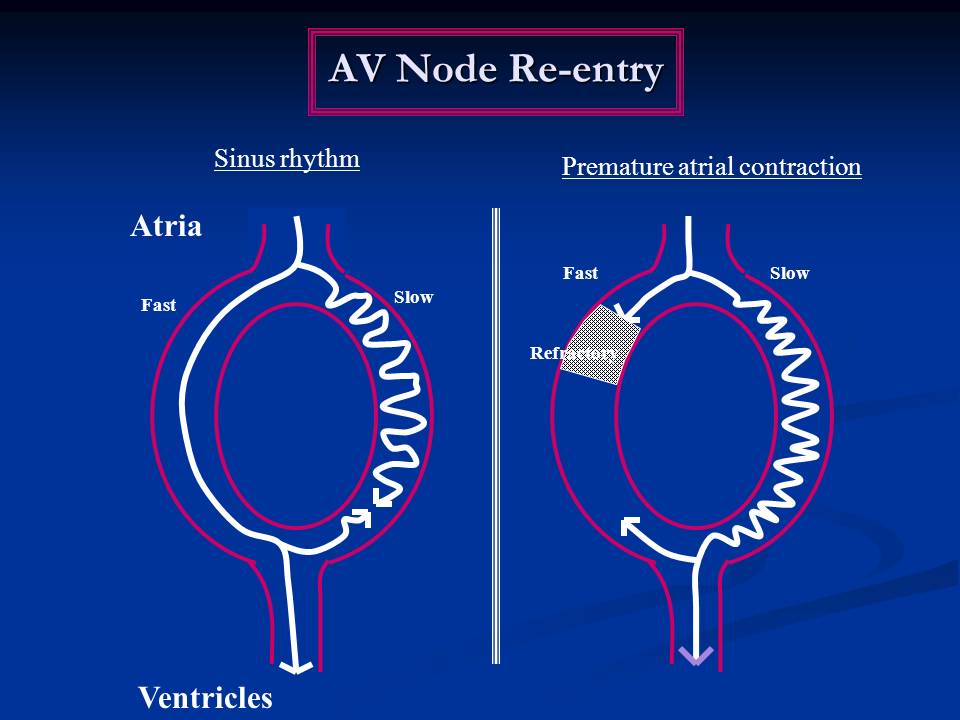
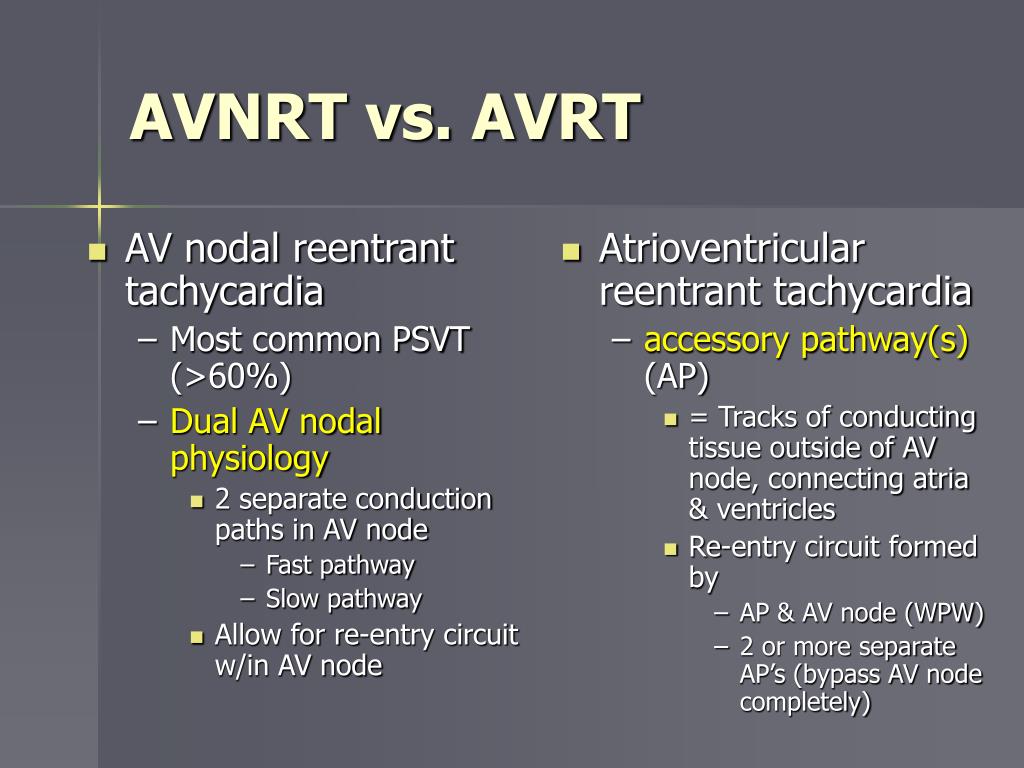
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (ie it originates above the level of the Bundle of His) and is the commonest cause of palpitations in patients with hearts exhibiting no structurally abnormality. Clinical Features of AVNRT

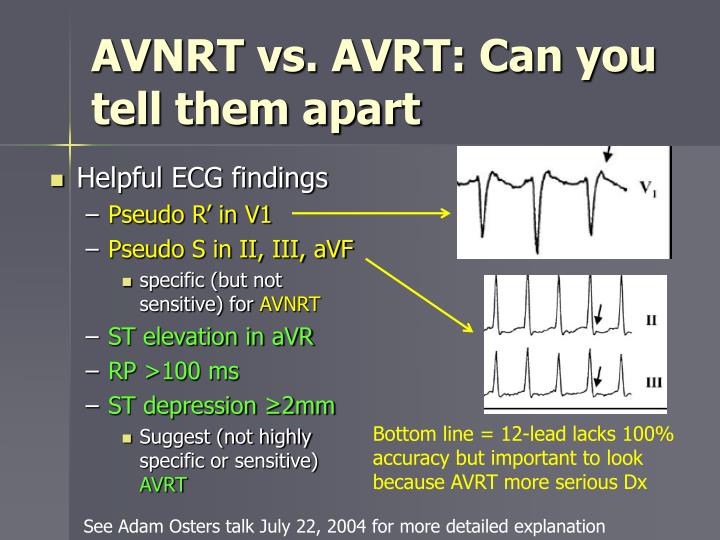
Differentiating Atrioventricular Reentry Tachycardia and Atrioventricular Node Reentry
Overview What is AVNRT? Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is the most common kind of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) due to an extra electrical pathway. SVT is a heart condition that makes the heart suddenly beat much faster than normal. A normal heartbeat is about 60 to 100 beats per minute when a person is at rest.
PPT Arrhythmias The Good, the Bad and the Ugly PowerPoint Presentation ID6582309
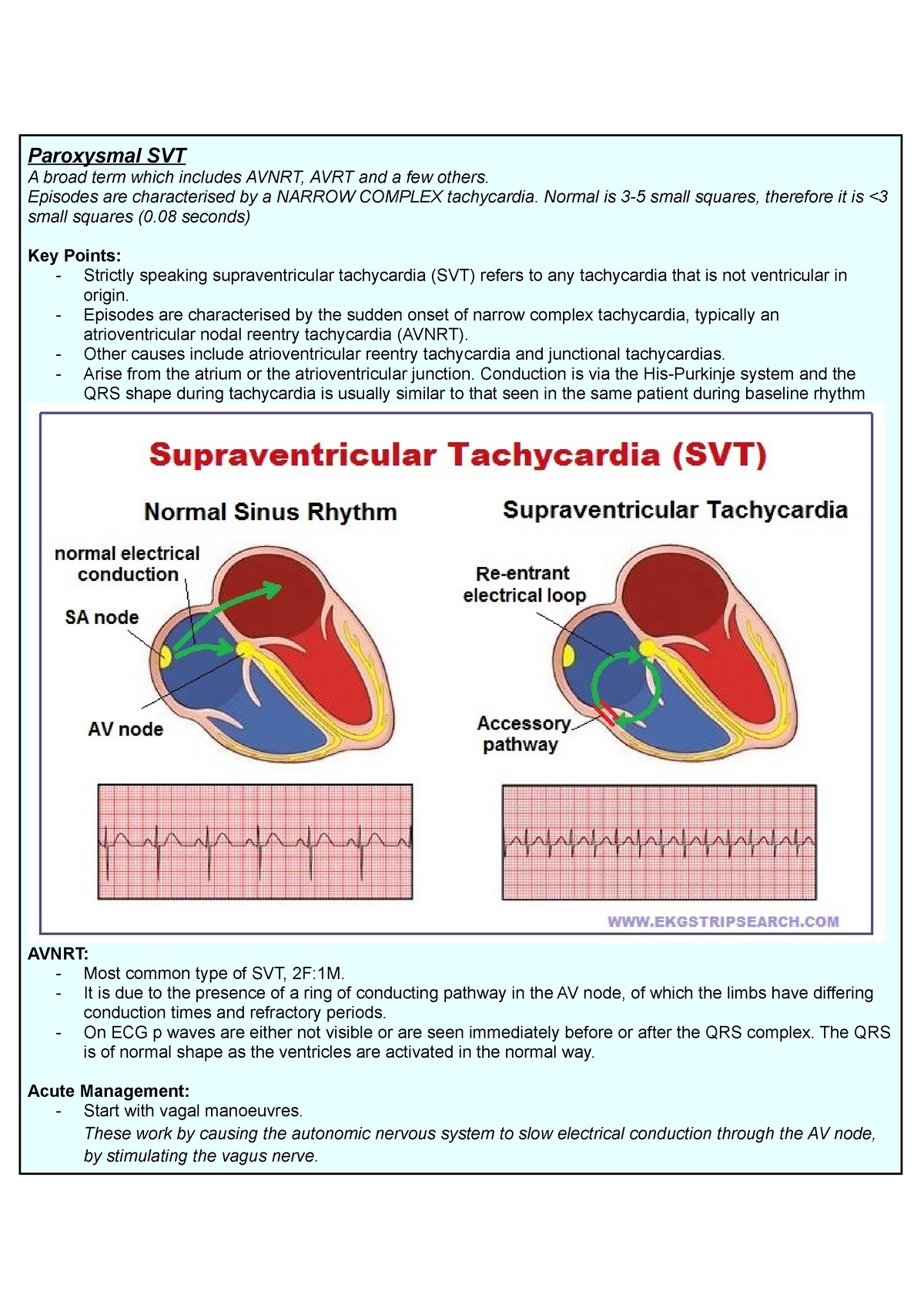
ECG Presentation Typically, AVNRT is a narrow-complex tachycardia, ie, QRS duration <120 ms, unless aberrant conduction, which is usually of the right bundle-branch type, or a previous conduction defect exists. Tachycardia-related ST depression and RR-interval variation may be seen.
Differentiation between AVNRT and AVRT_advanced lecture
Current maneuvers for differentiation of atrioventricular node reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) and atrioventricular reentry tachycardia (AVRT) lack sensitivity and specificity for AVRT circuits located away from the site of pacing.

Differentiating Atrioventricular Reentry Tachycardia and Atrioventricular Node Reentry
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is a term that refers to SVTs with abrupt onset and termination. AVNRT is a reentrant tachycardia that utilizes the AV node and perinodal tissues to sustain tachycardia. AVRT is a macro-reentrant tachycardia that utilizes an accessory pathway to create a circuit involving the ventricle.
PPT Narrow Complex Tachycardias PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID456264
The atrioventricular node and bundle of His are normally the only communication between the atria and the ventricles. The atrial impulse must pass through the atrioventricular node, which delays the impulse due to its slow conduction, before the impulse may reach the ventricles.

SVT (AVRT, AVNRT) For DO, MD, NP, PA [Part 3] YouTube
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a regular supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) that results from the formation of a reentry circuit confined to the AV node and perinodal atrial tissue. Because of its abrupt onset and termination, AVNRT is categorized as a paroxysmal SVT (PSVT).
Supraventricular Tachycardias Paroxysmal SVT A broad term which includes AVNRT, AVRT and a few
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf HHS Vulnerability Disclosure The atrioventricular (AV) node is a subendocardial structure located in the inferior-posterior right atrium.
PPT Narrow Complex Tachycardias PowerPoint Presentation ID456264
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is the most common form of regular supraventricular tachycardia and is routinely treated with catheter ablation (CA). AVNRT most commonly affects young and middle-aged otherwise healthy adults; females are more frequently affected than males.[1][2]
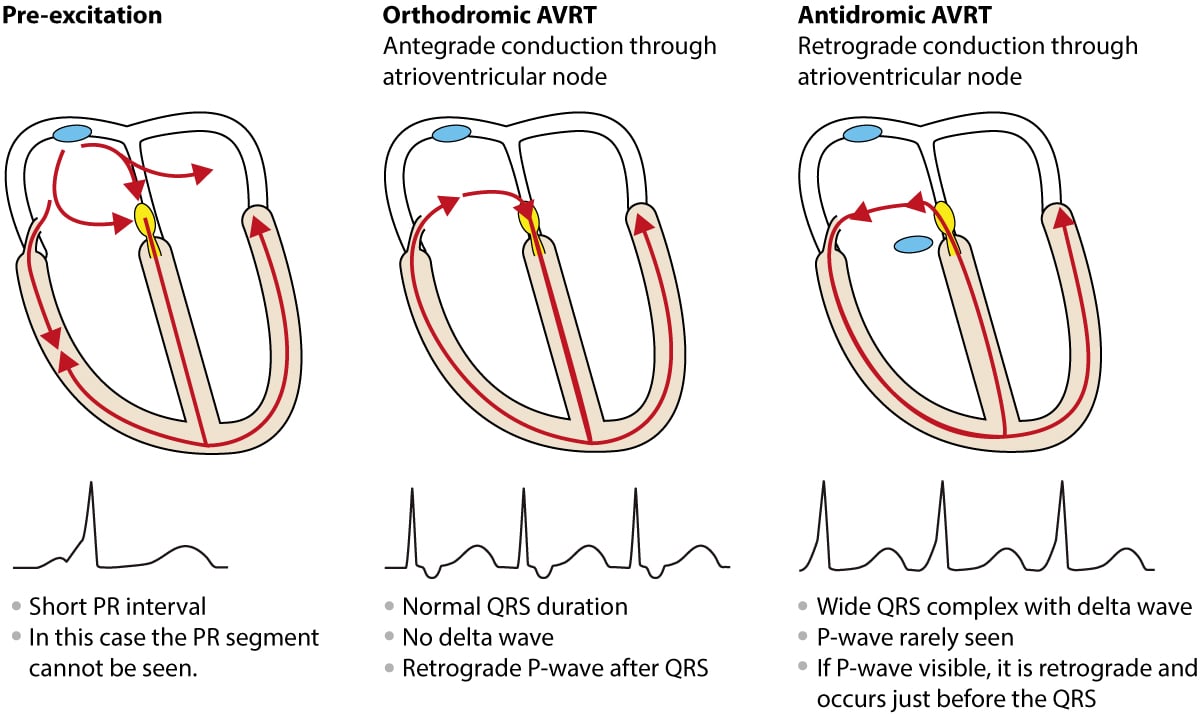
Figure 3. Antidromic and orthdromic AVRT. ECG learning
Atrial flutter Inappropriate sinus tachycardia Sinus node reentrant tachycardia Irregular Atrial Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter (variable block) Multifocal atrial tachycardia Regular Atrioventricular AVRT AVNRT Automatic junctional tachycardia AV Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT)

Preexcitation, Atrioventricular Reentrant (Reentry) Tachycardia (AVRT), WolffParkinsonWhite
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a common tachyarrhythmia occurring in all age groups, from children to elderly. AVNRT is common also among individuals who are healthy. This arrhythmia typically starts and terminates very abruptly.

Treatment for AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT) in Washington DC & Maryland
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is an arrhythmia frequently encountered in an otherwise healthy patient population. Catheter ablation should be considered as an initial treatment choice in symptomatic patients with AVNRT, given the high success rate and low risk for complications.

Differentiating features of AVNRT and AVRT Download Table
When AVNRT and AVRT are compared, symptoms appear to significantly differ. Individuals with AVNRT more frequently describe sensations of "neck pounding" that may be related to pulsatile reversed flow when the atria contract against a closed tricuspid valve.
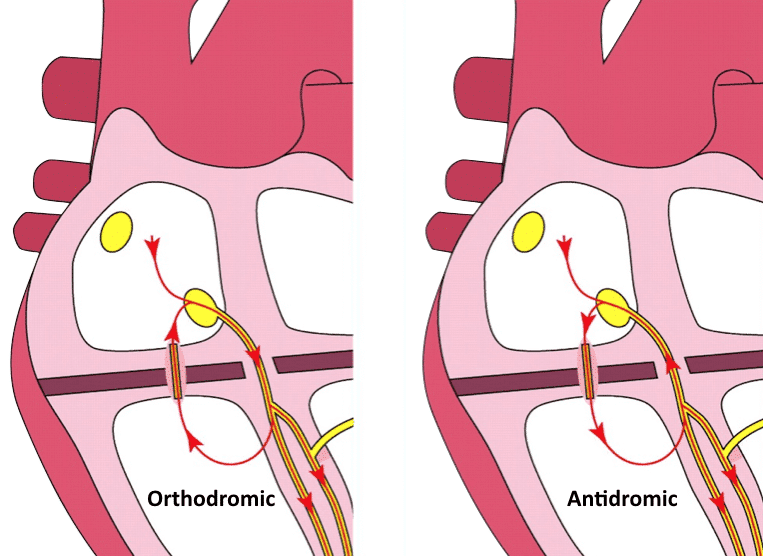
Preexcitation syndromes • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
The two main forms of tachyarrhythmias that occur due to accessory pathways are discussed separately — see atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia (AVRT) and atrial fibrillation/flutter in pre-excitation. Overview of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome